Project Archive (pre 11/2014)
- Identifying attractive application fields and developing commercialization strategies for the microScint technology developed by CERN
- Teezeit
- CodeAbroad
- Exploring New Application Fields for the iContour Technology
- ams technology – “Time of Flight Measurement”
- Innovative e-Biking concepts for future mobility
- Future Smart City Solutions
- Augmented Reality at CERN - The Personal Safety System
- Finding Commercially Attractive Applications for the Diaphragm System
- ESA & RUAG - Finding commercially attractive applications for the multi layer insulation
- ECOP INDUSTRIAL - Heat Pump for Industrial Purposes
- BUTLERS! - The travel simpleflyer
- Pennsylvania State University - Ideas for improving GCEC Conference Interaction
- BANK OF TOMORROW
- 7TSO Diagnostic GmbH
- Identification and Evaluation of New Application Fields for CERN’s Optical Data Transmission Technology
- OpenDoor
- Buttonz
- New application fields for the CVD diamond detector Technology
- Cutting Edge Tumor Recognition – A Business Model for PETs
- Shaping Atlas’ Future – Finding new ways for R&D collaborations between CERN and external partners
- Innovative solutions for Magna‘s new hybrid system 2.0 deriving from user needs
- Carbon fiber – Searching and evaluating business opportunities for the material of the future
- ATLAS Pixel Detector
- Mirovar - Intelligent Energy Management System
- A Protein Chip for the Early Detection of Cancer
- MOS - Magnetooptical Switch
- Bayer HealthCare - Overcoming the Hurdles to Increase the Utilization Rate of Oral Contraceptives
- TUW RACING : 3DGE Formula car
- CERN - Micro Patern Gaseous Detector Technology for Air Cargo Inspection
- Smart Sensing - Technological Competence Leveraging of Miniature Chemical Sensors
- MedAccess
- Leveraging HV-CMOS Technology
- Technological Compentence Leveraging of Mores ® - Optical Sensor Technology
Wintersemester 2011/12
Executive Summary
Background
Global warming is becoming more and more a real threat for mankind and environment. Additionally, it is obvious that traditional fuel resources are limited. Legislation has already reacted to these major challenges and is continuously tightening up on CO2, exhaust gas and noise emission limits. Furthermore, a growing population accompanied by an increased demand for mobility is obvious.
The automotive industry is already reacting and several results are yet in market or right now in development. One approach to meet these challenges will be hybrid and electric vehicles, getting more and more market shares in future. But there is still a potential for innovative solutions for future hybrid vehicles.
The project therefore focuses on the end customers’ needs for hybrid vehicles and the customer perception of cleaner mobility concepts as well as expectations regarding hybrid vehicles of today and tomorrow.
Project goal
The project challenge was to understand the current perception of hybrid cars from the drivers’ point of view (actual consumers and non-consumers) and develop future concepts for hybrid cars that meet the consumers’ needs.
Approach and methodology
The project goal was achieved by applying the method of Design Thinking to gather an in-depth understanding of the customers’ mind, challenge existing solutions and generate future ideas and solutions up to functional models and prototypes. Students from different disciplines and backgrounds (design, business, and engineering) worked in interdisciplinary teams to make use of and integrate different perspectives regarding the innovation challenge.
The project was structured into two major phases: an (1) in-depth market and consumer analysis (research phase) followed by (2) an idea and concept generation phase including the visualization of the concept as functional models or prototypes.
Research Phase
Ideation and concept development Phase
Results
The inal concepts comprise fuel-eficiency tools for hybrid cars that are implemented into the software of the cars, ranging from advanced usage of global positioning systems that calculate more fuel eficient routes concerning actual and real-time date, to car-to-car communication between hybrid cars in order to better collect relevant data. Also, the inal concepts include solutions for the information overload of hybrid cars during trips, collecting data during drives and aggregating them to relevant driver journals.
All solutions generated have been evaluated and tested by users and other stakeholders confronted with today’s solutions and its challenges.
If you are interested in more details concerning the inal concepts and prototypes, please contact the project partner directly.
Cooperation Partner
MAGNA Powertrain AG & Co KG
Plant Lannach
Industriestraße 35
8502 Lannach
ÖsterreichContact Person
Markus Bichler
Advanced Development
Hybrid-/EV-Powertrain
MAGNA PROJECT HOUSE EU
E-Mail: markus.bichler@magnapowertrain.com
Student Team
Patrick Bonhold
Marius Höbenstreit
Julie Charlotte Kainz
Marion Kanalz
Thomasz Kilarski
Peter Perstel
René Prinz
Thomas Rath
Bernhard Scheiblauer
Walter Sinn
Florian Sturm
Sommersemester 2011
Executive Summary
On the basis of a deep analysis of strengths and pain points of the current management of the Fuzzy Front-End (FFE) of innovations at A1, this project provides a recommendation on how to optimize the structure of the FFE management for a more successful idea selection, evaluation and new product development.
Background, Problem, Goal:
“If Siemens only knew, what Siemens knows.” – Comprehensive knowledge management is one of the most challenging tasks in a multinational company like Siemens consisting of 405,000 employees dispersed globally and organized in numerous departments and subdivisions.
There is no doubt that an efficient tool to exploit these synergies would significantly support and facilitate innovative activities.
As early as 1998 an intranet platform called TechnoWeb was designed to do precisely that – facilitate networking and problem-solving. After the emergence of Web2.0 it was re-launched as TechnoWeb2.0. Very much like a company version of “Facebook”, this platform allows its 11,000 users to create profiles, set-up and participate in networks and finally contact experts via urgent requests.
When the project partner approached the Institute of Entrepreneurship and Innovation they had observed that while there were certain activities that already worked well on the platform there was little innovative activity taking place at the TechnoWeb. Consequently they were looking to lift this platform to the next level by putting in place an environment that would also foster innovation.
Thus a cross-functional team of three master and bachelor students was assembled in order to develop a specific concept to foster idea generation on “TechnoWeb2.0”.
Methodology
As a basis this team studied pertinent literature in order to identify general success factors of such platforms. With this knowledge an in-depth analysis of the actual platform, TechnoWeb2.0” was conducted in the course of which 22 semi-structured interviews with users were held. 5 major barriers to innovation were identified. With this knowledge in mind the team looked at other innovation initiatives, like Idea Contests and Innovation Jams, within Siemens to get a sense on how these challenges were tackled there. In a third step 5 interviews were conducted with software suppliers who provide companies with state-of-the art software solutions. Finally the team interviewed 7 companies using the offered software
solutions placing special emphasis on how the Siemens specific challenges were tackled.
Drawing from these four sources a threephased recommendation was designed which will enable Siemens to unleash the vast potential on TechnoWeb2.0.
Findings & Analysis
During the conversations with users, moderators, innovation managers, etc. the following five challenges were identified:
Lack of perceived benefit
Users often do not see a direct benefit of contributing to the platform.Lack of management support
Management has not yet put emphasis in communication that usage is desired.Internal competition for resources
A fierce internal marketplace often prevents co-operation and free-revealing.Trade-Off between openness and focus
The open nature of the platform hinders focused discussions to occur.Cultural setting
Siemens employees are often not used to engaging online using communication facilities such as posting and commenting.
Recommendation
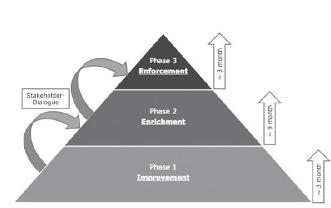
After thorough analysis the following threephased approach was designed.
[Abb. vgl. unten]
In a first phase key functionalities like the search function of TechnoWeb2.0 will be improved. This is to immediately increase perceived benefit for all users. These improvements can be implemented for the entire “TechnoWeb2.0” community.
In a second phase certain innovation addons are introduced in order to tackle the challenges. These include:
Closed rooms and layers of confidence
The ability to create private communities and control the information available to the individual members.Structured Feedback
A more structured way to give and receive
feedback on ideas by including experts.Direct Communication tools
The ability to directly chat, call or have a video conference with the members of a network.Sponsors and Moderators
Management lending their name to certain networks to boost their legitimacy as well as appointed moderators to lead the discussions.Teaming function
Ability to better identify and contact experts of unrelated fields of expertise through TechnoWeb2.0
Users confronted with the concept, knowledge gained from literature research as well as the analysis of well-functioning platforms in other companies all indicate the necessity and importance of the above factors. The described add-ons will first be tested in a pilot phase open only to selected users. This way costs can be limited and the functionalities can be efficiently tailored to the user community.
In a final and third phase the improved and enriched platform is promoted. Through word-of-mouth recommendation a bandwagon effect will kick in, thus increasing participation, activity and eventually innovation on the platform.
In order to assure the highest possible degree of satisfaction of all stakeholders a continuous stakeholder dialogue will accompany the three phases.
Cooperation Partner
Siemens AG Österreich
Siemens Chief Technology Office
Open InnovationContact Person
Fabrizio De Pasquale
Tel: +43(0)5170722969
E-Mail: fabrizio.de-pasquale@siemens.com
Student Team
Fani Christofi
Johannes Greller
Selene Horner
Nino Mori
Isaac Newton Acqua
Pablo Piñero
Appendix: Figures
Wintersemester 2012 / 2013
Executive Summary
Abstract
Since 1966, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has been partnering with people at all levels of society to help drive and sustain the kind of growth that improves the overall quality of life. In Uzbekistan the UNDP concentrates on the areas of poverty reduction, environment, energy and democratic governance. Within its project “Social Innovation and Volunteerism”, UNDP focuses on sustainable development and enabling environment for Uzbek youth. Concerning the youth bulge (around 60% of population are below 30), the high rates of youth unemployment and lack of infrastructure and possibilities in rural areas with a high density of young people, UNDP considers the engagement in social innovation and entrepreneurship an excellent chance for empowering people to have a positive impact on their society. However, as the field of social innovation/entrepreneurship is rather unknown and new, in July 2012 the UNDP started its two-year project “Social Innovation and Volunteerism in Uzbekistan“. The goal of the project is to establish an environment that will enable the Uzbek youth to actively engage in social innovation. In collaboration with Vienna University of Economics and Business, a student team coached by the Institute of Entrepreneur- ship and Innovation was assigned to research on the topic and provide the UNDP with an understandable explanation as well as suggestions on how to implement concrete methodologies at place and start creating a sustainable social innovation environment in Uzbekistan. The outcome of the project is a coherent 4-stage model which includes methodologies for the different stages of social innovation.
Initial Situation
Uzbekistan is a post-Soviet country in Central Asia, struggling with its transition to a market economy. Major challenges for Uzbekistan are its high unemployment rate, the discrepancy between urban and rural areas, a low stage of technological development and limited infrastructure, as well as a high emigration of knowledge.
To address these issues the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Uzbekistan launched a two-year project in July 2012, which aims at empowering Uzbek young and well-educated people to engage in social innovation and social entrepreneurship.
Project Target
Expected outcome of the project is a thorough explanation and under- standing of social entrepreneurship and innovation as well as an implementation plan for a selected number of methodologies to support social innovation efforts in Uzbekistan. The implementation of these methods is expected to be the first step in the creation of a social innovation environment in Uzbekistan.
Procedure & Methodology
Theoretical Background
In order to provide the UNDP with an elaborate and comprehensible definition of social innovation and social entrepreneurship, we con- ducted an extensive secondary research including approximately 30 sources.
Identifying Supporting Methods
As next step, we further explored 120 different methodologies which can support and encourage social innovation. According to the pro- posed selection criteria we chose the most relevant ones and illustrated them in a coherent table.
Designing an Implementation Plan
As last step, we suggested a 4-stage model to the UNDP. This model includes the most relevant and suitable methodologies for supporting social innovation in Uzbekistan, and goes from workshops to create initial social innovation awareness and knowledge up to the creation of a place where potential social entrepreneurs can meet, establish a community and collaborate in order to target the most problematic social issues of the country.
Results
Firstly, a definition of social innovation has been elaborated. The team focused on providing the UNDP with sufficient information about what social innovation is and which methods are suitable to support social innovation as such, as well as which stages are to be gone through to reach a highly developed social innovation environment.
Secondly, a four-stage model for the implementation has been developed. Stage 1 concentrates on the creation of social innovation knowledge among the target group. The “workshop” aims to create the needed knowledge for social innovation and encourage the diffusion of the learned approaches into rural areas. Stage 2 focuses on raising the awareness of the topic as well as further diffusion of social innovation knowledge to rural areas, supporting the micro-workshop initiative of stage 1. It is essential to use different PR tools in order to promote social innovation in different offline and online channels. Stage 3 is dedicated to finding interested partners who are willing to actively engage in social innovation by providing resources and who may act as business angels. In order to accomplish this goal, existing networks and communities in Uzbekistan have to be identified and contacted. Stage 4 addresses the question how to bring the social innovation community together at one place as there are no physical points of contacts for different social innovation actors in Uzbekistan yet. This facility acts as a „club house“ where potential social entrepreneurs/innovators can work together on SI business ideas, meet with possible investors and use the needed equipment. This method has been particularly successful in other countries worldwide, „the HUB“, being a best case example.
Cooperation Partner
United Nations Development Programme
(UNDP) Uzbekistan
41/3, Mirabad street
Tashkent, 100015, UzbekistanContact Person
Emiliya Asadova
E emiliya.asadova@undp.org
Student Team
Julia Arrighi
Andrea Barth
Andreas Brunauer
Katarína Dudžáková
Sommersemester 2011
Executive Summary
Fundamental research has always been under pressure to justify its spending of public money by transferring the knowledge gained to the economy and promote growth by innovation to the benefit of the entire public. This is particularly true for CERN, one of the world’s largest and most renowned centers for fundamental physics. Situated in Switzerland, CERN is famous for its Large Hadron Collider - the world’s largest and highestenergy particle accelerator. The organization has a strong interest in finding alternative applications in the private sector for the technologies developed as a side product of its scientific experiments.
One of those is the Quantum Dosimeter, a new generation radiation detector able to determine the dose, dose rate and composition of radiation with utmost precision.
This project aimed at the identification and evaluation of alternative application fields for the Quantum Dosimeter technology. Two of the newly identified fields – environmental monitoring and location monitoring of critical places for terrorism prevention – have been analyzed in greater detail. Both markets were found to be compatible with CERN’s strategic requirements and highly attractive in terms of competitive forces and their market potential. A brief outline of recommended market entry strategy has been developed for each application field.
Initial Situation
In the last few years the pressure on CERN to justify its spending of public money on non-applied science has increased along with the costs of the Large Hadron Collider. Therefore, CERN is highly interested in transferring its developed technologies to the private companies to boost the economy and thus prove the benefits of fundamental research to the public in order to secure further funding.
One of those technologies is the Quantum Dosimeter (QD), a radiation measurement device based on a radically new method. In order to find potential markets for this invention CERN has turned to the Institute of Entrepreneurship and Innovation.
Project Target
The project’s goal was to find as many alternative application fields as possible, to evaluate them and to propose commercialization strategies for the most attractive application fields. Fields with strong public impact were preferred by CERN. Financial gain was considered to be secondary. Military applications were explicitly excluded.
Approach and methodology
The project was conducted based on a user-community based approach to technological competence leveraging. The method consists of the following steps:
1) Identification of the main benefits by interviewing current and potential users:
2) Systematic search for additional application areas via a combination of interviewing and pyramiding:
3) Analysis of the commercial potential of identified applications:
.
4) Outline of a commercialization strategy for the most promising applications:
Results
In the course of this project, 28 potential application fields were identified, ranging
from material testing, space telescopy brick production, personal dosimetry, to contamination controls and cancer treatment programmes.
The two most promising fields with respect to strategic fit and the need for a new solution (as provided by the Quantum Dosimetry technology) turned out to be the stationary environmental monitoring and monitoring of critical places for the purpose of nuclear terrorism prevention (airports, hubs, mass events).
The field of environmental monitoring is recommended for immediate market entry. There is a potential development partner interested in the licensing of the technology. The market potential sums up to € 300 million; the current market volume is estimated to be € 45.5 million, leaving considerable space for growth, which is predicted to be 9% from 2011 till 2014. No major technical adaptations of the Quantum Dosimetry technology are required; the Quantum Dosimetry device is almost “ready to use”.
Monitoring of critical areas for security purposes is recommended for later market entry. The market is in an early development stage, posting impressive annual growth rates of 24%. The market potential for airports alone is estimated to amount to € 99 million; the potential market volume ranges from € 6.6 to € 20 million (most likely € 12.5 million). Various large players of the sector have already expressed interest in the cooperation with CERN. Legal framework is the major driver of the market, so that further development is dependent on the national and international security regulations.
Cooperation Partner
European Organization for Nuclear Research
Knowledge Transfer Group
CERN CH-1211
Genève 23
SwitzerlandAnsprechpartner
Giovanni Anelli
Tel.: +41 76 487 8858
E-Mail: Giovanni.Anelli@cern.ch
Student Team
Valentin Aschermann
Christoph Bitzner
Claudia Ilsinger
Patricia Klopf
Bernhard Sauerteig
Maria Sergeeva
Barbara Weissenböck
Sabrina Zischka
Wintersemester 2008/2009
Executive Summary
Background and Product Description
Many Biotech Startups and SMEs develop novel drugs for treatment of severe asthma. However, they lack medical competences and infrastructure regarding testing and researching efficacy for their developments. Additionally, many big companies in the pharmaceutical industry outsource the testing of drugs for asthma treatment.
OHME BioTech serves these companies with high quality testing, research services and its unique expertise in treatment of severe asthma. It has developed a novel system in order to test the effectiveness and reverse action of potentially new drugs. This system aims at minimizing risk of those drugs that are not yet approved. In addition, it operates an IT supported collaboration platform, which offers efficient and secure knowledge management, project management, reporting and communication to its customers.
Business Model
OHME BioTech has established a strategic partnership, which allows them to offer their services at a very competitive price. It generates its contract-based revenues from short-term orders. Strategically, license based revenues shall be generated from long-term co-development activities with its customers in order to target a sustainable cash flow and foster growth. In addition, short-term contracts serve as first customer contact and feed long-term co-development relationships. The services offered by the collaboration platform foster tight customer relationship and customer retention.
Unique Selling Proposition
The USP is based on a unique expertise in the treatment of severe asthma, on high quality testing and on high research capabilities. These are all based on expertise from long term research in immunology and cell biology. Furthermore, The IT supported collaboration platform enables the customers of OHME BioTech to accelerate their business development due to instant and cost effective access to medical experts and facilities.
Market Analysis
90% of the asthma drug market is highly saturated and is covered by best seller drugs of big pharmaceuticals. However, the remaining 10% niche represents 30 million people worldwide who require expensive treatment due to absence of a drug which effectively treats severe asthma. This niche is penetrated by Biotech Startups and SMEs, which lack medical testing and research expertise and thus outsource these activities.
Moreover, the financial crisis forces them to enter co-development partnerships. Total R&D expenditures had an annually growth rate of 11% and the outsourcing market volume was € 220 million in 2007.
Competition Analysis
The pharmaceutical outsourcing market is covered by two big companies, which have a market share of nearly 50%. However, the remaining 50% are shared among small companies each contributing less than 0.3% of total market. Hence, small companies compete successfully against the two leaders. OHME BioTech has a unique expertise in treatment of severe asthma and targets customer proximity with low prices. These aspects grant them a unique position in the market.
SWOT Analysis
The main strengths of OHME BioTech are its unique expertise in treatment of severe asthma and its cost efficient infrastructure due to the strategic partnership. Its main weaknesses are the single area of competence in severe asthma and the un-predictable license-based revenue model. OHME BioTech faces opportunities due to the current financial crises, which forces Biotech Startups to enter co-development partnerships and a general trend to outsourcing testing and research activities. However, these opportunities are confronted by threats that have their origin in the publication of former research in severe asthma. Furthermore, there might be threats due to the academic activities of the founders as well as the unknown security of Biotech Startups.
Financial Analysis (Break-Even)
OHME BioTech will break even in the first quarter of the third year. These calculations are based on revenues generated from short term orders excluded all license-based revenue. In the fourth year, all investments are fully returned through the cumulated income. The cumulated revenues in the first 5 years will ammount up to € 3 million. From the beginning on fixed costs will be respectivly high at €330.000 per year while average costs per contract are low at € 5.500.
Recommendation
Based on the findings of the market research a Go-Decision is recommended. However, the establishment of many co-development partnerships is crucial for the success of this venture. It would guarantee substantial growth as well as a diversification of testing areas and research competence. Moreover, setup and operation of a sophisticated collaboration platform is a complex task and must be planned meticulously in order to avoid reverse effects.
Cooperation Partner
Dr. Michelle Epstein
Dr. Oskar Hoffmann
Medical University of Vienna
VetWIDI Forschungsholding GmbH
University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna
Student Team
Stefan Glanz
Camillo Pachmann
Hannes Stauss
Wintersemester 2010/11
Executive Summary
Solvster provides a crowdsourcing platform for „open“ online product development to match consumer needs with companies in a direct way. A large online community combined with Solvster’s professional project management provides an innovative solution to increase product development efficiency in the “fuzzy front end” of the new product development process. The close integration of users increases product success and significantly reduces time to market and cost to market.
Solvster mainly targets innovative small and medium enterprises in a variety of B2C industries, such as Fast Moving Consumer Goods, Product Design, Information and Communication Technologies, Entertainment & Lifestyle and Banking.
Product
Solvster’s innovation project management specializes in the “fuzzy front end” of the product development process. Despite of high expenditures for market research activities, up to 80% of new products fail, mainly because they do not meet customer’s needs. By integrating a large user base in the product ideation and evaluation phase, Solvster does not only increase new product success, but also significantly reduces time and cost to market. Cost savings of up to 300% can be achieved. One of Solvster’s key resources is its crowdsourcing platform which consists of the following three modules:
Trend Quest
: Community members comment on and evaluate current market trends.Idea Quest
: Based on the most relevant trends, users generate ideas for new products and services.Shop Quest
: The top ideas are further evaluated in a virtual market test.
Business Model
Solvster offers a packaged solution including all three modules combined with its innovation management services. To meet customer needs, each Quest is also offered separately. There will be a fixed basic price for each module and a variable price that depends on the outcome (e.g. number of ideas in the IdeaQuest). Solvster is pursuing a penetration pricing strategy and offers its service at a lower price than its main competitors.
Target Market and Competition
Solvster mainly targets small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in the German speaking region. Solvster’s target group are innovative SMEs who are open for cooperation with customers. This represents a market potential of € 780 million in the German speaking region in 2012. Solvster’s solution is applicable in many different B2C industries such as Product Design, Information and Communication Technology, Entertainment & Lifestyle and Banking.Solvster competes with other online crowdsourcing platforms and with market research institutes. Most direct competitors focus on idea generation while Solvster additionally offers a market simulation tool. Currently, there are only a few direct competitors because the market is still very young and unconsolidated. The annual growth rate is 10%.
Marketing
Companies
: The main promotional tools for targeting paying companies will be personal selling and PR activities. New customers will be acquired through networking activities and congress and fair visits.Community Members
: Solvster will mainly use social media and viral marketing techniques to establish and to enlarge the community base. Solvster’s user community will be the key factor for the company’s success. Therefore, high attention will be given to community management. To motivate users to participate, prize money and gift prizes will be awarded.Company, Team and Development
Solvster was established in 2009 as a Austrian GmbH domiciled in Vienna. Dietmar Eglhofer, Ulrike Eglhofer and Martin Benesch occupy the positions of strategy, administration and sales. The main team functions will be in Business Development & Marketing, Community Management, Project Management, Sales and IT Support. Solvster has already conducted different pilot projects with companies of various industry sectors.
Financials
Revenues will rise to € 7.2 million in 2014. To expand the business high expenditures in marketing and HR are necessary which finally result in an annual surplus of € 700,000 in 2014; a ROI of 25 % will be generated.To meet these goals, Solvster requires € 1.4 million in bank loans and € 3 million in deposits of silent partners.
Cooperation Partner
Solvster GmbH
Fasangasse 9
2103 Langenzersdorf
ÖsterreichAnsprechpartner
Mag. Dietmar Eglhofer
Tel: +43-664-3433237
E-Mail: dietmar.eglhofer@solvster.com
Student Team
Sabrina Dietl
Lili Gao
Nikita Gorlov
Alexandra Klopf
Andreas Lechner
Wintersemester 2009/2010
Executive Summary
Research on antibodies is the key to developing medicines to some of the world’s gravest diseases.
The market for monoclonal antibodies (mAb) represents the fastest growing market segment within the research industry. Antibodies are a major part of the human defence system. When considering the number of proteins predicted in the human and other genomes, current available mAb are far from meeting demand and represent a bottleneck for biotech research activities.
Company
Within this market CROMAB will be established as a Rijeka based monoclonal antibody trading company which identifies, produces and markets a unique collection of mice monoclonal antibodies for the basic research community. CROMAB will be a part of the scientific network which offers the opportunity to precisely meet customer demands and scientific trends. It bears the opportunity of finding the best antibodies with remarkable sales potential. Professor Jonjic is the key person with years of experience as well as an outstanding reputation within the scientific community. All antibodies that have been developed until present are ready for market entry.
Product
Naturally antibodies are an important part of the immune system. They can be used to investigate viruses and on the long run to fight diseases. Antibody-based medicines are a fast growing segment of the pharmaceutic industry and have proven to be very successful treatments. CROMAB offers an excellent collection of monoclonal antibodies for research purposes. The offered antibodies will be on the one hand produced by CROMAB and on the other hand by other companies, that produce mAb. Thus CROMAB will also act as a broker. In only a few years of existence the Center of Proteomics has achieved to develop a unique collection of mAb of excellent quality that can be used to investigate the function of various viruses that widely spread among world populations.
Market
According to The Antibody Report 2009 he antibody market is a fast growing market with growth rates of 9% in 2008. In 2010 monoclonal antibodies are predicted to generate 3 billion € in revenue. In 2010 CROMAB will have a 0,003% market share due to its position as a niche player. The market is expected to grow further especially as a result of the growing demand for antibody-based therapeutics which requires intensive research on antibodies.
Marketing
The most reliable marketing tool in the biotech industry is word of mouth propaganda. With Professor Jonjic as the key person of CROMAB and his very well established scientific network and reference customers, CROMAB will definitely gain recognition very fast. Although CROMAB will offer its assortment worldwide from day one, most requests are expected for Europe since Professor Jonjic’s network is based in this area. Furthermore CROMAB will sign up to the best known antibody search engines on the internet, for example antikoerper-online.de, where antibodies can be found quickly whenever there is demand. Signing up to these internet-based search engines will enable CROMAB to increase its degree of popularity.
Financials
Set up costs are very limited. During the incorporation phase of the first 2 years the financial demand is projected with €35.000 mainly personal costs, keeping required assets at €10.000. Since CROMAB will be located in the Science and Technology Park of the University o Rijeka personnel and production facilities will be rented by the Center of Proteomics which helps us to keep costs at a minimum. The company expects to reach break even in the 2nd year of its existence. Within 4 years the cumulated profit will under the most likely case exceed €100.000. Sales will rise at an average rate of 25,5% and are expected to keep this growth rate in the years to come.
Summary
CROMAB has great potential for establishing itself in the fast growing biotech market, precisely the research industry. Since it is very unlikely that the demand for antibodies will ever be fully met, constantly growing revenues can be expected. The expertise of Professor Jonjić combined with the closeness to the University of Rijeka and the scientific community will contribute to CROMAB’s success.
Cooperation Partner
Prof. Dr. Stipan Jonjic
Ani Gerbin, Dipl.–Bw.
Center for Proteomics,
University of Rijeka
Student Team
Walter Pongratz
Magdalena Stejskal
Vera Woldan
Simone Tömördy
Christian Lindner
Wintersemester 2002 / 2003
Product
Due to the deregulation of the European energy market, the rising number of suppliers and consumers, the increased load on an existing network and the resulting volatility of the security devices fault current incidents have risen to higher levels, the market has a need for a new device. This protective device known as the Superconducting Fault Current Limiter (SFCL) has been designed by VA TECH SFCL to reduce fault current levels in existing electricity networks
Cooperation Partner
DI Herbert Piereder
(Corporate Marketing & Strategy, Head of Division)
DI Paul Barnfather
(Strategic Technology)
VA Tech AG
http://www.vatech.at
Student Team
Amira Gutmann
Mario Freissl
Markus Krischmann
Susanne Reiss
Sommersemester 2003
Executive Summary
Introcuction
The background of our project is the framework of the business idea “Superconducting Fault Current Limiter”. During the last term, our team was responsible for the creation of a busi-ness plan for the SFCL. Following this, the challenge in the actual term was to create a mar-keting concept for the market entry of the SFCL in Great Britain, which shall be the first mar-ket to be conquered. The marketing concept includes three mainpoints as follows:
Key Account Customers
Following the research work of the last term we identified the potential key account custom-ers for the SFCL in the UK. Data and background information of these key accounts was filed. Following this, the necessary human ressources for the sales team were calculated. In addition the window of opportunity for the SFCL for each of the key account customers is shown. Finally alternative customers – beside from network operators – were identified as to show the potential of the SFCL in other markets.
Proof of Technical Efficiency
The second mainpoint of the marketing concept deals with the technical efficiency of the product that has to be prooven to the customers. We identified the need of establishing a reference installation within the network of one of the potential customers as to be in a posi-tion to proove technical efficiency as well as stated capacity of the product. This mainpoint deals with structure and prerequisites of the sub-project “reference installation”. Questions like “which customer is suitable for installment of a prototyp?”, “which data shall be generated and which information will be communicated to the customers?”, “who will be responsible for the reference installation project within the team?”, and so on, are answered.
Proof of Financial Rentability
For a sucessful marketing of the Superconducting Fault Current Limiter it is finally necessary to communicate the financial rentability of the product to the potential customers. Therefore a table, showing the lifecycle costs of the SFCL (in form of calculation of discounted cash flows relating to the investment) was prepared. The sales team can use these sheets to compare the purchase of a superconducting fault current limiter with the one of a new circuit breaker, as to explain the financial rentability to the customers.
Cooperation Partner
VA Tech AG
DI Herbert Piereder
DI Paul Barnfather
http://www.vatech.at
Student Team
Amira Gutmann
Susanne Ines Reiss
Mario Freissl
Markus Krischmann
Wintersemester 2012 / 2013
Executive Summary
About the Company
Mountaineering S.r.l. is an engineering consulting company located in Bolzano, Italy. It offers services in the field of natural hazard consulting, natural hazard research and hydrological analysis in the mountainous regions.
Project goal
In the wake of diminishing revenue growth, the company is seeking new markets to expand to. Because of the geographical location in the Alps, the DACH-region constitutes a potential target market for Mountaineering. The task of the project was to analyze the German, Swiss and Austrian market and highlight the most interesting region.
Approach and Methods
The Project consisted of two major phases. The first part was the analyses of the DACH-markets. This analysis included among others PESTEL and Porters Five Forces. The recommendation constituted the second part of the project.
Market Analysis
Germany
In comparison to the other two markets, Germany is the least developed market. The government just recently started their first large projects, for example creating hazard maps for large areas in Bavaria. In addition, the supply side of the market is not as saturated as in the other markets. This is why projects are often conducted with the help of companies or small engineering offices from Switzerland, who are at the forefront of the industry. However, this shows that Mountaineering has a good opportunity of entering the market directly, trying to gain brand recognition in the market to attract contracts. Another possibility would be to cooperate with regional engineering offices, which acquire the contracts through their well-connected networks and then execute the projects with the help and expertise of Mountaineering.
Austria
Natural hazard mapping is currently a major concern of the Austrian authorities, and therefore a promising market for Mountaineering. Additionally, the ÖBB (State-owned railway company) is constantly building new railway tracks in mountainous regions, where Mountaineering‘s services are required, due to the strict law in Austria, regarding environ- mental compatibility. The market consists of many smaller engineering offices and governmental institutions, providing equal or similar services as Mountaineering. On the other hand, those firms and institutions are often interested in partnerships in order to create a mutually beneficial relationship.
Switzerland
Switzerland has the strictest regulations concerning natural hazard protection in the DACH-region. Since the whole country has already been hazard-mapped, the potential revenue in Switzerland is limited. Moreover, Switzerland prefers regional companies. It is very hard for international companies to receive orders, because of the very strict regulations of the individual cantons. However, there are a lot of interesting companies looking for partners in order to improve its performance. Especially in the research field, this can be a very attractive option to enter the Swiss market.
Recommendation
In conclusion it can be said that, the three markets are still in their development phase, as no clear market leader could be identified, and the markets are still expanding. This is also due to the fact that these services distributed very regionally, with a lot of small companies and engineering offices taking up the biggest chunks of the markets. How- ever, this also gives Mountaineering the opportunity to set foot in these markets through directly attracting contracts while advertising their sophisticated measurement methods to gain recognition or by partnering with regionally known engineering offices, who have good connections to the public administrations in the specific regions, while Mountaineering provides them with the needed expert knowledge and expertise.
RecommendationIn conclusion it can be said that, the three markets are still in their development phase, as no clear market leader could be identified, and the markets are still expanding. This is also due to the fact that these services distributed very regionally, with a lot of small companies and engineering offices taking up the biggest chunks of the markets. How- ever, this also gives Mountaineering the opportunity to set foot in these markets through directly attracting contracts while advertising their sophisticated measurement methods to gain recognition or by partnering with regionally known engineering offices, who have good connections to the public administrations in the specific regions, while Mountaineering provides them with the needed expert knowledge and expertise.
Cooperation Partner
Mountain-eering S.r.l. Via Siemens 19
39100 Bolzano
ItaliaContact Person
Matteo Dall’Amico
T +39 0471 068226
E matteo@mountain-eering.com
Student Team
Maximilian Lunacek
Stefan Röll
Joachim Treiber
Lars Vajen
| Sommersemester 2014 |
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Project Partner and Background
The Fraunhofer Society is Europe’s biggest organisation for applied science. Fraunhofer acts as a development partner and offers the needed expertise for development of the technology solutions with partners from different industries.
Despite the vast number of protective systems on the market, the rate of severe injuries and often death due to accidents involving motorcyclists is very high. A rising safety consciousness in the motorcycle community and the capability of Fraunhofer to develop unprecedented products where the main reasons to address this subject.
Project Goal
The goal of the project was to develop smart protection for motorcycle riders. The first task was to gain proper insights of different types of riders and their driving habits.
Approach and Methodology
In order to reach the goal of the project a specific method, the “Design Thinking” approach, had to be used throughout the project. It is an iterative and human centred approach focusing on interdisciplinarity. Students from the Institute of Entrepreneurship and Innovation (WU) worked together with a student of Mechanical Engineering from TU, Vienna.
Research
Research was conducted through observations, self-test and a substantial secondary research.
Key insights are needs of the customer that where not discovered before. Understanding the key insights was the team’s first task. They were derived from interviews (n=53), observation and self-tests (n=63) and secondary research (n=23). Afterwards, the information was evaluated and clustered based on strategic fit with the project goals and market relevance of the solution and eventually approved by the project partner.
The most important key insights are:
Lack of situational awareness and overview (especially in urban areas)
Insufficient visibility of the motorcyclists
Need for better motorcycle control
Mistakes by other traffic participants.
Ideation
The second phase of the methodology starts with ideation. This is the part in which the group members try to find a solution (product/system) that will meet the chosen key insights. A creativity workshop helped the group to understand and apply different methods of creating ideas based on the chosen key insights. The ideas were visualized, discussed and shortlisted in order to be taken to the next phase.
Solution
To meet the needs of urban motorists on city tours (chosen target group, as agreed with the project partner), the complexity of the product should be as low as possible to allow convenient day to day application. Based on community data a system that gives the rider information on the perfect driving speed as well as warning the motorcyclists from potential threats was presented. In order to accomplish this in a way that is aligned with user needs, prototypes were built and presented to the users. Their feedback was used to adapt the prototypes and develop the final product.
Cooperation Partner
Fraunhofer Venture
Hansastraße 27c
80686 München
bjoern.schmalfuss@zv.fraunhofer.de
www.fraunhoferventure.de
Student team
Benjamin Mörzinger
Christoph Rathmayer
Alexandra Olsacher
Alisa Eresina
Daniel Huber
Ervin Kajevic
| Sommersemester 2014 |
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
We are developing a concept to be the #1 provider of a fresh and creative "to go" fruit & vegetable juice selection with a city-wide network of unique retro stores in highly frequented spots.
The Problem
Health consciousness and an active lifestyle are huge trends. Urban citizens are more than ever interested in products that support this way of living. However, in fast-paced times like these, time and convenience issues make it difficult to live a healthy life.
The Customer's Need
Time and convenience issues result in people being bound to their specific location of occupation when it comes to the choice of food or drinks. Surveys among more than 170 potential customers have shown that the target group is extremely inflexible in terms of mobility (i.e. actively going to a store further away) and thus "availability" in the sense of having a store around the corner is the key to a purchase.
The Solution
In order to serve our customers with a healthy lifestyle product, we are creating a unique buying experience by transforming raw fruits and vegetables in front of our customer's eyes into fresh juices and smoothies.
Ordinary as well as unconventional, healthy, green fruit juice and smoothie creations are served within a simple „to-go“-concept, offering only low seating capacity. The experience will be topped off with a unique, retro and hip in-store design that reminds our customers of an old "Presserei" (i.e. pressing plant).
What is more, we will offer our products at highly frequented locations across Vienna in order to make them available to the broadest audience in the most convenient way possible and thus taking into account crucial time and convenience issues.
The Vision
We are following a 4 step approach in achieving our goal of providing „the city‘s best juices“. Our journey will commence with the step-by-step opening of branded stores city-wide.
This will be followed by operating mobile sales stalls at selected events that cater to our target group.
Once "fruchtpresserei" as a brand is established, we aim to position our products with high-end restaurants and bars via selected partnerships.
The medium- to long-term expansion plans are based on scaling up a franchise model in other urban areas in and around Austria.
Contact Person
Sebastian Greiner, BSc (WU)
Co-Founder & CEO
sebastian@greiner.or.at
Student Team
Sebastian Greiner (WU)
Josef Mayer (WU)
Georg Steigberger (WU)
Thomas Wohlfahrtstätter (WU)
Wintersemester 2013 / 2014
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Background and Problem Statement
The Fraunhofer Institute for Reliability and Microintegration (IZM) is a German research institution specializing in packaging technology and system integration of multifunctional electronics. As a leading body in 3D Integration with Through Silicon Via (TSV), an open knowledge technology, Fraunhofer IZM is looking for new application fi elds, where implementers of sophisticated sensor systems may benefi t from the institute’s extensive know-how during the shifting process from conventional to TSV-manufactured systems.
Project Goal
The aim of this project is defined as finding and evaluating promising application fields for 3D Integration with TSV.
Method
The underlying methodology is a ‘User Community-Based Search Approach to Technological Competence Leveraging’, a four-phase attempt to hurdle the shortcomings of conventional technology transfer practices. In short, this advance is achieved by systematically addressing the creativity inherent in communities of current and potential technology users. These communities are consulted to help identifying the technology’s benefits, finding and evaluating additional fields of application and, finally, developing a feasible business model.
Results
From 39 user interviews conducted during the initial phase of the project, six core benefits of 3D Integration with TSV have been identified. A total number of 58 interviews with users, technology experts and problem holders across eight different countries generated 20 ideas for potential application fields, including: computer tomographs, vehicle dynamics control systems, optical gauges, spectroscopic devices and biosensors.
Upon discussion with the project’s steering board, the fields of “Computed Tomography” and “Inertial Sensors for Vehicle Dynamics Control Systems” have been selected for an in-depth market and competitor analysis.
(1) Computed tomography utilizes computer-processed X-rays to scan the interior of an object. Using TSV-based sensor systems, computer tomographs achieve a higher image resolution, while image noise, X-ray dose and power consumption can be greatly reduced. With an annual production of 16M sensors and a growth rate of about 10 per cent, the CT market is considered highly attractive.
(2) Inertial sensors measure static and dynamic motion inside vehicle dynamics control (VDC) systems. Primarily, TSV technology allows for a significant miniaturization of these systems, addressing the severe lack of space inside vehicles’ control devices. Current annual VDC system production amounts to 40M units with a growth rate of 3-5 per cent. In the long run, VDC system installation rates are expected to rise from today’s 50 to almost 100 percent.
Based on these results, commercialization strategies and business models have been developed for the two application fields. As concerns computed tomography, Fraunhofer IZM may guide producers of CTs and CT sensors through the implementation process of TSV-based equipment. Therefore, the specific market consists of the four main players: General Electric, Philips, Siemens (with AMS as supplier of sensors) and Toshiba. In the case of inertial sensors, Fraunhofer IZM may serve as a know-how provider for manufacturers of VDC systems while collaboratively preparing TSV-based systems for serial production. Entry into this market is to be conducted by directly approaching the three main producers of VDC systems: Bosch, Continental and TRW.
Cooperation Partner
Fraunhofer-Institut für Zuverlässigkeit und Mikrointegration IZM
Gustav-Meyer-Allee 25
13355 Berlin
Deutschland
Dipl. Ing. Thomas Fritzsch
thomas.fritzsch@izm.fraunhofer.de
Student team
Heinrich Ameseder
Olivia Eberhard
Benjamin Hartl
Markus Presle
Valentin Priesner
Niklas Raschhofer
| Wintersemester 2013 / 2014 |
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Status quo
The Aichelin Ges.m.b.H. Mödling, leading producer of industrial furnace systems for heat treatment of metal components, operates in a market characterized by growing saturation and tight margins. This and a significant dependency on the automobile industry led to the decision to search for new fields of application in order to diversify the portfolio.
Project Target
The target of the project was finding alternative and previously unexplored application fields for Aichelin’s furnaces, know-how and heat-treatment processes. Furthermore, the project team was to look for new materials to which those processes could be applied and to subsequently determine in which industries those materials are used. Out of these areas, possible new and promising markets had to be selected.
Method
In order to achieve the desired results, the approach “Technological Competence Leveraging” was applied. This method allows generating completely new ideas and discovering innovative application fields. The approach can be divided into four steps:
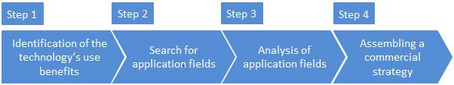
Results
The four steps were characterized by intensive research. The results of the conducted processes can be summarized as follows:
Interviews conducted: 128 in steps 1/2 and 50+ in steps 3/4
Communities contacted: 17 user communities
Industries covered: over 40
Application fields found: 82
10 top application fields
After consulting with the project partner, the following three application fields were analyzed in further detail:
Pyrolysis for CFRP recycling: Aichelin’s heat treatment technology can be applied to the recycling of the ever-increasing amount of CFRP (Carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer).
Hardening of titanium aluminide for turbine blades: Turbine blades made out of titanium aluminide are predicted to become standard in medium-haul commercial jet production. Aichelin could provide apt furnace systems for these high-quality components.
Production of tempered safety glass: The demand for tempered safety glass is increasing in various industries, particularly the construction sector. Glass finishing requires a heat-treatment process that could be provided by Aichelin.
Subsequently, a market analysis (including an environment analysis, a competitor analysis as well as a SWOT analysis) was conducted for all three selected application fields in order to recognize the potential of the ideas.
Based on these analyses, the team created respective business models and market entry strategies to illustrate the realizability of the new application fields for the project partner.
Cooperation Partner
Aichelin Ges.m.b.H.
Fabriksgasse 3
A-2340 Mödling
ÖsterreichMag. Wolfgang Brosche, MS
wolfgang.brosche@aichelin.com
www.aichelin.at
Student team
Bereuter Theophilo Antonio
Handler Florian Christian
Koch Maximilian
Leimert Hannah
Malzer Mauricio
Paier Raphael
Wintersemester 2011/12
Executive Summary
Background
Airbus is a leading aircraft manufacturer whose customer focus, commercial know-how, technological leadership and manufacturing efficiency have propelled it to the forefront of the industry.
Passenger comfort has always been a major consideration at Airbus in order to ensure the highest levels of comfort, services and efficiency and the best possible passenger experience. Not only are Airbus cabins innovative and attractive, they are continuously being improved to offer travelers the quietest, most comfortable and enjoyable journeys. Especially the needs of elderly people (e.g. poor visual, acoustic or motion abilities) are demanding and call for future concepts. Taking the trend of a continuously aging population into account (2030: 65+ >40% of total population worldwide expected), solutions are even more relevant.
Project goal
The challenge was to understand and develop innovative future cabinconcepts and functional models for elderly passengers with specific needs (e.g. poor visual, acoustic and motion abilities).
Approach and methodology
The project follows the Design Thinking method – a structured and versatile human-centered approach to generate innovative new product and service concepts up to new business models. Students worked in interdisciplinary teams from different disciplines (business, engineering, medicine, design, history).
The project was structured into two major phases: an (1) in-depth research phase followed by (2) a structured ideation, concept development and prototyping phase.
Research Phase
An analysis of market, needs and trends was conducted by means of secondary research, interviews (100 target group interviews, 20 expert interviews (e.g. docs-on-board, light security, training centers, safety operators)), observations (e.g. airport, mock-up center, workshop), and self testing. Out of the irst research 15 key insights were identiied.
Ideation and concept development Phase
Based on the indings of the irst phase solutions for the major key insights were to be found. Starting with an idea generation and collection phase, the ideas and concepts systematically were tested and challenged in an iterative process leading to a visualized and multiple-tested functional model or prototype.
Results
The inal concepts comprise solutions for improved mobility of (elderly and average) passengers concerning the seating area and individual storage room for personal belongings of passengers in the seating area.
All solutions generated have been evaluated and tested by users and other stakeholders confronted with today’s solutions and its challenges.
If you are interested in more details concerning the inal concepts and prototypes, please contact the project partner directly.
Cooperation Partner
AIRBUS Operations GmbH
Contact
Cabin Innovation Strategy
Cabin Product Strategy & Concepts (TBCUI)
Matthias Zachaeus
E-Mail: Matthias.Zachaeus@airbus.com
Tobias Tamm
E-Mail: Tobias.Tamm@airbus.com
Student Team
Christof Brandtner
Andreas Buranich
Marcel Ertl
Elias Ferihumer
Marlene Hanke
Andreas Hirt
Daniela Leitgeb
Markus Neubauer
Felix Petzenhammer
Kristoph Retezár
Philip Marcus Schreiner
Roman Schweiger
Markus Wild
Sommersemester 2011
Executive Summary
Abstract
On the basis of a deep analysis of strengths and pain points of the current management of the Fuzzy Front-End (FFE) of innovations at A1, this project provides a recommendation on how to optimize the structure of the FFE management for a more successful idea selection, evaluation and new product development.
Starting Point
Mobilkom Austria and Telekom Austria have merged recently and formed together A1 Telekom Austria AG. A1 is operating in the telecommunications industry, which is characterized by constantly changing consumer needs and fast technological changes. In order to outperform its competitors, the company has to react quickly to market changes and is forced to develop an idea today for a product that is still desired at the time of its launch. These environmental factors cause the high importance of innovation at A1. The company operates both on the B2C as well as on the B2B level.
The Fuzzy Front-End (FFE) of innovations is defined as the period between when an opportunity is first considered and when an idea is judged ready for development and comprises of idea generation, product definition and project evaluation.
Problem definition and project goals
One particular challenge A1 is facing after the merger is the management of innovations. As the current new product development process is a compromise between the former processes of the two single companies, there is no unified new product development process at A1 at the moment, and the company lacks a structured and unified idea generation and evaluation process. In particular, A1 struggles to (1) enable employees to bring their ideas to the table, (2) get ideas from different channels pool potential ideas and review them , (3) provide a platform for objective evaluation and (4) push promising ideas into the product development process.
The main goal of this project is
to give a recommendation for the management of the fuzzy front-end system of the A1 Group.
The following sub-goals assist in solving the main goal:
(1) Finding and monitoring pain points in the current process,
(2) aligning the existing initiatives with a structured and transparent process for idea generation and evaluation
and (3) create a structured and transparent fuzzy front-end management.
Approach
In a first phase a thorough
literature research
was conducted. The project team searched for best practices for the FFE management in other companies. Secondary data was derived from case studies, business reviews, academic publications and personal contacts. Fourbest case examples
(BMW, Google, IBM, Swarovski) were chosen to underline the final recommendation.As-is analysis:
An as-is analysis was conducted with the focus on those business units and initiatives having the highest relevance for innovation activities at A1. The departments identified are Customer Service, Business Marketing and Small & Residential Marketing, and the initiatives are InnoLab and Wanted Next Level. Information about the departments and the initiatives, respectively, was collected in 21 semi-structured interviews with employees of A1. Preliminary findings were tested in further follow-up interviews. The insights from the interviews lead to a detailed and holistic picture of the current FFE management at A1 and served as a basis for further actions.
In the second phase, the project team scrutinized the pain points and strengths of the current FFE management discovered in the interviews according to the New Concept Development Model suggested in literature. The knowledge about best practice examples and the information gathered from the literature research were brought together to provide a sound recommendation for A1.
Results and Recommendation
The following main pain points in the current FFE management at A1TA were identifies:
• Hardly any top management support concerning employee driven innovation
• No culture and awareness for innovation
• Unstructured idea generation process
• Lack of communication – no exchange of ideas
• Strong informal network needed to push ideas
• Product managers are mainly responsible for innovations
• No “face” for innovation
Taking into consideration the boundary conditions at A1, i.e. lack of resources (manpower, time), the following recommendations were developed. Also, currently existing innovation activities and initiatives at A1 were taken into account as each of them brings its contribution to the innovation process with its own advantages.
The recommendation is built like a modular system, leaving the choice to A1 what modules to implement and what pain points to solve with the specific modules. At the basis of the system lies “The Core”, actions to foster innovation among the employees of A1and to establish an innovation culture. In addition, three modules are suggested.
Module A - Innovation Platform and Innovation Team (pain points addressed: no culture/awareness for innovation, unstructured idea generation process, lack of communication, strong informal network needed, product managers mainly responsible, no “face” for innovation): The central element is a platform allowing employees to enter their ideas and to discuss ideas of others. For the support of the platform, we suggest a full-time team of three people whose task it is to moderate the platform, update information, screen and choose the ideas, give feedback, establish personal contact to the various innovation initiatives and have a broad overview over the innovation activities going on within A1.
Module B - Innovation Coaches in all departments (pain points addressed: no culture/awareness for innovation, lack of communication, no “face” for innovation): Line managers like department or group managers take over the role of an innovation coach. They act as a first point of contact for employees in innovation topics.
Module C - Innovation Workshops (pain points addressed: lacking top management support, no culture/awareness for innovation, lack of communication): One-day workshops are held for employees interested in innovation. The formal opening held by the top management is complemented with the actual workshop, consisting of different tables with different questions and topics, inviting employees to join and discuss.
The project team suggests the implementation of the innovation platform together with the innovation team. Although the three different modules may be introduced separately, the entire package is the optimum way to structure the FFE management at A1.
Cooperation Partner
A1 Telekom Austria AG
A-1020 WienContact Person
Mag Stefan Hauer (CCO Area,
Department for Strategy and Planning)
Student Team
Andreas Martinek
Niklaus Mauthe
Christina Mayr
Elisabeth Danninger
Linda Horner
Sommersemester 2012
Executive Summary
Initial Situation
The Squiggle Motor is the world’s smallest linear piezo actuator, whichwas developed at New Scale Technologies, Victor, USA. The directproject client was ams, a multinational semiconductor manufacturer,based in Unterpremstätten, Austria. As ams holds a main stake in NewScale Technologies, it seeks to successfully commercialize the SquiggleMotor.The Squiggle Motor itself is currently mainly used in mobile cameratechnology, but its smallness, preciseness and direct linear movementsqualify the motor for further application in more diversified, high marginmarkets.
Project Target
The project’s objective was to find a large number of novel and distantapplication areas and to evaluate their commercial attractiveness. Aftera detailed analysis of the most promising ideas, suitable market entrystrategies were developed.
Procedure and Methodology
The E&I-based 4-phase-framework “Technological Competence Leveraging”served as a guiding structure throughout our project:
1. Identification of the benefits delivered by the technology
4. Development of a commercialization strategy for the most promisingapplications
Results
As a starting point, 50 ideas of application for the Squiggle Motor wereidentified through brainstorming activities, existing user interviews orthrough crowd sourcing in online communities. In a continuous processof a total of 110 interviews with potential users, the identified applicationareas were assessed based on predefined criteria. Seven ideas,which were rated the highest in the dimensions of benefit relevance andstrategic fit, were positively validated.This structured approach for processing the collected information aboutpotential application areas, served as a basis for decision-making at theproject’s steering board meeting. Three application areas were chosenfor an in-depth analysis, which consisted of three different tools:
• Market analysis
From these analyses, suitable business models with a strong focus onthe value chain and the revenue stream were derived for the chosenthree applications:
Actively Stabilized Handheld Tool
Myoelectric Prosthetics
Micro modeling
Cooperation Partner
New Scale Technologies, Inc.
121 Victor Heights Parkway
Victor, NY 14564
ams
Tobelbader Strasse 30
A-8141 UnterpremstaettenAnsprechpartner
Dr. Michael Leitner
Marketing Director – ams
Tel.: +43 664 1424896
E-Mail: michael.leitner@ams.com
Student Team
Patricia Backhausen
Dominik Franke
Verena Haller
Teresa Havlicek
Stefanie Heidinger
Felix Hlatky
Hans Kaufmann
Oliver Lehner
Alex Mihajlovic
Michael Neuwirth
Philip Schnattinger
Philippe Thiltges
Wintersemester 2010/11
Executive Summary
Kurzbeschreibung:
“Magna Powertrain AG” is a subsidiary of the multinational group “Magna International inc.” Magna International is one of the largest and most diversified suppliers in the world,
focusing in complete vehicle engineering and assembly operations. The company has 245 manufacturing operations and 80 product development, engineering and sales centers in 25 countries on five continents. The objective of this project was to find new application fields for the vacuum pump technology, which is an essential component built into break boosters of private vehicles. One student team of 8 persons was assigned to systematically search for and evaluate potential applications for the vacuum pump technology and to develop actionable commercialization strategies. Magna strives for a 10% increase in turnover in non-automobile sector by 2015. Therefore the cooperation with the WU is regarded by Magna as a project of great importance in order to expand into new profitable business fields.
Initial Situation
Electric vacuum pumps already exist in different models for various purposes on the market. In automobile industry vacuum pumps are built into most modern hydraulic brake systems, reducing necessary operating force on the brake pedal. Diesel and modern engine applications don‘t have enough depression to support the break booster and for that reason a vacuum pump is needed. As the technology in the automobile industry advances, vacuum pumps are required to be light and efficient. Magna designed a novel vacuum pump concept to fulfill all these requirements and to substitute common used mechanical pump types.
In addition to its automobile business, Magna intends to diversify its product range, targeting new application areas other than vehicle industry. Magna currently follows a cost leadership strategy in order to achieve optimum product distribution. Mass markets are therefore more suitable according to business strategy. In order to achieve the company’s objective, a cooperation with students of WU was formed, who assist Magna in searching for new commercially attractive applications for its vacuum pump. Technical assistance during the project time period was offered by DI Dipl. Kfm. Wolfgang Weber and DI Andreas Auinger. The
initial briefing revealed essential insights for under-standing the technology and its benefits from the producer’s perspective.
Project Target
The aim of the project was to find as many new and attractive application areas for the vacuum pump technology as possible, to evaluate these opportunities and to develop a commercialization strategy for the most promising ones. Thereby, the potential application areas should not only offer solutions to specific problems in these areas, but also be in accordance with the strategic orientation of Magna Powertrain.
Procedure and Methodology
The project was based on a communitybased search process for technological competence leveraging. This process consists of four interrelated steps.
1. Identification of the main benefits by interviewing current and potential users.
2. Systematic search for additional application areas via a combination of pyramiding and broadcast search
3. Analysis of the commercial potential of identified applications
4. Assembly of an actionable commercialization strategy for the most promising applications
Results
By interviewing 10 current and potential users of the vacuum technology, four main benefits (from a user’s perspective) of the technology were revealed: (1) low weight components, (2) compact de sign with minimum space requirements, (3) very easy to transport (4) high precision of engine control system. Based on these abstract ‘user benefits’, more than 40 potential fields of application were identified in the course of approx. 200 interviews. In accordance with the project partner, the four commercially and strategically most promising application fields were selected for further analysis. Consequently, detailed market-, competitor- and SWOT analysis were conducted, resulting in the most promising suggestions. In 2009 the global market value for the focal marked investivated is estimated to be between $ 1,1 billion and $ 1,8 billion, increasing steadily with an annual growth rate of approximately 8% due to demographical development in the western society and increasing demand for an effective solution. Hence the market value is expected to continue its expansion within the next five years to around $ 2,8 billion. The US market is by far the largest, which accounts for 60% of the global value. The European market, especially Italy, France and Germany are expected to show excellent performance in the future. This suggestion to Magna is based on the commercial attractiveness in the industry to ensure maximum return on investment.
In terms of the other 3 application fields, valid information regarding market value could not be obtained via online data base. Thus interviews by experts were conducted to estimate the market situation. As the results of the interviews, a critical size of the market could not be identified fitting Magna’s mass market strategy.
Cooperation Partner
Magna Powertrain AG
Steyrer Straße 32
4300 St. Valentin
AustriaAnsprechpartner:
DI Andreas Auinger
Harald Bachmayr,
DI(FH) Dipl.Kfm.(FH) Wolfgang Weber
Student Team
Aumüller, Christine
Baumann, Gregor
Hauswirth, Timo
Häder, Janine
Klosterer, Claudia
Kössl, Ernst
Witibschlager, Philipp
Zhan, Jun
Wintersemester 2012 / 2013
Executive Summary
Abstract
The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) was founded in 1954 and is one of the world’s largest research laboratories. The organization is dedicated to research in fundamental physics, with the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) being the most famous experiment at CERN.
The objective of this project was to find new application fields for the Gigabit Data Aggregator, a data processing chip (FPGA) originally invented at CERN for the use within the LHC. A student team was assigned to systematically search for and evaluate potential applications for the Gigabit Data Aggregator technology and to develop actionable commercialization strategies.
Initial Situation
The Gigabit Data Aggregator is an invention allowing the processing of vast amount of heterogeneous data at high speed with full integrity. It is recently in development at CERN in order to cope with the requirements of constantly processing vast amounts of data at the LHC in general & especially within the ATLAS project.
Besides using technology for its scientific experiments, CERN has the intention to transfer in-house knowledge to the general public; in the year 2000, CERN has introduced an active Technology Transfer policy, aiming to maximize the technological and knowledge return to CERN member states and to promote CERN’s image as a centre of excellence for technology development.
In order to make the Data Aggregator valuable for the general public, new application areas for this technology are needed, in particular at- tractive ways of implementing this new technology in existing markets. Furthermore, CERN aims at finding alternative application areas for the Gigabit Data Aggregator in order to find potential development partners to share costs of development, manpower & technological know-how.
Project goal
The aim of the project was to find new and attractive application areas for the Gigabit Data Aggregator, to evaluate these opportunities and to develop a commercialization strategy for the most promising ones. Thereby, the potential application areas should not only offer solutions to specific problems in these areas, but also be in accordance with the strategic orientation and background of CERN as the project partner.
Methodology
The project was based on a community-based search process for technological competence leveraging. This process consists of four interrelated steps.
Identification of the benefits delivered by the technology
Systematic search for additional/diverse application areas via a combination of pyramiding and broadcasting
Analysis of the commercial potential of identified applications
Development of an actionable commercialization strategy for the most promising applications
Results
By interviewing 18 current and potential users of the Gigabit Data Aggregator, four main benefits (from the user’s perspective) of the technology were revealed: (1) capability to process vast amount of data at high speed, (2) possibility to individually tailor the algorithms (customizability), (3) capability to process heterogeneous data at 3 different stages:
1. Decoding, 2. Processing and Filtering, 3. Repackaging and (4) guaran- tee of full data integrity, meaning that no data gets loss in the process.
Based on these abstract ‘use benefits’ about 60 potential fields of application were identified in the course of app. 85 qualitative interviews. The suggestions ranged from the use of the Gigabit Data Aggregator in DNA Sequencing to Astrophysics. In accordance with the project partner, the three commercially and strategically most promising application fields were selected for further analysis:
(1) Financial Market Data Mining
Research showed that there are four major players in the market with a combined market share of more than 80%. All the identified trends in this industry confirmed that demand will considerably increase in the next five to ten years – based on the best scenario, a quantity of approximately 155 units can be sold in five years whereas in ten years already 855 aggregators will be demanded, reflecting the extremely high market growth.(2) Public Video Surveillance
Current statistics show that the global CCTV market will reach $19 billion in 2013. Considering that 28% of the cameras are network cameras, in which the FGPA chip could be integrated, approximately 1.4 million units could be sold in 2013. The growth of the market is considered to rise significantly over the following years (25.31% for network cameras), also due to higher public security awareness.(3) Algorithmic Trading
Currently, FPGA technology is not that widely spread in algorithmic trading because of the novelty of the technology in this field and traders are quite cautious using it. However, FPGAs have the opportunities to outperform CPU software systems due to superior speed. What is more, high frequency trade volume is expected to continue to grow in the next years so speed and capacity will be of substantial importance.
Cooperation Partner
European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) Genève 23
CERN CH-1211
Switzerland
Ansprechpartner
Philippe Farthouat (CERN) T +41 (0)22 767 6221
E Philippe.Farthouat@cern.ch
Heinz Pernegger (CERN) T + 41 (0)22 767 5847
E Henning.Huuse@cern.ch
Student Team
Viktor Aigner
Daniel Haas
Elizabeth Huzar
Paul Kapeller
Berid Lackner
Nikola Martinovic
Daniel Mikl
Vanessa Pinter
Alex Zuber
Sommersemester 2010
Executive Summary
jobsunited is an international online employment and career platform network connecting students/graduates, companies and universities in various countries in CEE. A new business model, which revolves around parts of the application process and an integrated matching algorithm, ranking applicants by their fit to the job, enables companies to find high-qualified students at reduced time and cost.
Product Description
jobsunited is an international online employment and career platform network, connecting students/graduates, companies and universities in various countries in CEE. The newly structured application process enables companies to invite the desired candidates to apply for the job immediately after advertising the vacancy. By using Europe-wide standardized attributes for education, work experience etc, students of all participating international universities can be compared directly. All candidates are matched and ranked according to their fit to the job by the means of these standardized attributes and companies on the other hand can see, who meets their requirements best and request those to apply for the job immediately. With jobsunited the duration of the whole application process is reduced by at least 53%. Partnerships for additional features (e.g. Online Assessment center) have already been established and implementation is technically feasible at any time. Serving as a perfect substitute for career centers, the platform is not just totally free of charge for universities, but they even have the possibility to receive a 30% commission of all revenues generated through their students. companies have access to highly qualified students from different universities and countries and students are provided with job offers from numerous countries on one single platform.
Market Entry
jobsunited will be first launched at the University of Liechtenstein. At the beginning of 2011 the platform will be implemented at 5 other European universities, where oral agreements already exist. Later in 2011 and 2012 jobsunited will be launched comprehensively in 6 CEE countries.
Business Model
Only companies have to pay fees for the services offered by jobsunited, while for students and universities, all services are completely free. In contrast to ordinary job platforms, the placing of job offers is free of charge at jobsunited. companies have to pay only in the event of any submitted application. Other services such as online assessment or advertising mails constitute additional sources of revenue.
Sustainable Competitive Advantages
jobsunited benefits from its first mover advantage as it is the first international and interconnected employment and career-centric platform network in Eastern Europe with a focus on students and graduates. jobsunited is completely free of charge for both, universities and job seekers and universities even earn money through the platform. Once implemented jobsunited, universities will face high switching costs in case of partnering with other platforms.
Market and Competition Analysis
Only those universities that are not equipped with a career center represent the target market of jobsunited. And for the time being, especially those universities situated in Central and Eastern Europe are being focused. In CEE, the market potential is extremely high since most universities there have no career centers. The countries of our interest are: Austria, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, Latvia and Hungary. Along with the need of companies for highly qualified staff and the need of students for work experience abroad, the market for online recruiting is steadily increasing. It is true that strong competitors such as Monster or Jobzippers.com have already gained a foothold on the market, but the product differentiation of jobsunited will substantially contribute to its successful launch and its desired market position.
Swot-Analysis
International connection and Europe-wide standardized attributes of applicants are the greatest strenghts jobsunited offers. In addition, jobsunited benefits of an extensive first mover advantage. However, bureaucracy can become a problem in the future. Nevertheless, favorable market opportunities, trends towards online recruiting and increased mobility of students provide jobsunited with a variety of great opportunities.
Financials
In the case of the most likely scenario the initial investments are expected to amortize as early as in the second business year of 2011. Considering the cost structure, it becomes evident that personnel and marketing expenses represent the major pools of costs.
Employees will be paid a bonus for achieving the targeted turnover. Furthermore, since the University of Liechtenstein is providing jobsunited with the necessary server and office, no substantial investments are needed at the beginning and the break-even point will be reached in 2011. Due to the fact that jobsunited is willing to accomplish moderate and stable growth and aims for upper quality job offers, all costs will be containable.
Cooperation Partner
Patrik Schneider
Marcel Vaschauner
Stefan Debortoli
Harald Schmidt
Ansprechpartner
Patrik Schneider
Marcel Vaschauner
Student Team
Roland Felber
Michael Forster
Chen Ji
Philipp Parrer
Thomas Wohlfahrtstätter
Wintersemester 2003 / 2004
Executive Summary
The service concept of stratCON consists of an integrated consulting and solution-competence provided by one hand. QPR ScoreCard and QPR ProcessGuide are business software tools. They are embedded in the whole process of analyzing, reorganizing and developing a strategy. The software is freely configurable and can be individually adjusted to every company’s needs. From 2004 onwards stratCON wants to provide these services in the Croatian market.
Cooperation Partner
StratCON Management Consulting
Mag. Wolfgang Bartholner
DI Walter Abel
www.stratcon.at
Student Team
Peter Brandhofer
Patrick Lobis
Lisa-Maria Mittmansgruber
Stefanie Schneider
Wintersemester 2012/2013
Executive Summary
Starting Situation
Ruse is one of the largest cities of Bulgaria and, being located directly at the Romanian border at the only bridge alongside the Danube connecting these countries, the main transit point to the north. Accordingly, it is one of Bulgaria‘s most important business centers and attracts international firms and business travelers. Additionally, it has a beautiful main square which is visited by tourists from all over the world. The Danube Plaza Hotel is situated in the heart of this town. However, in recent years losses have been generated. The student team therefore scrutinized a range of innovative business ideas for the real estate, concluding that a continuation of current activities offers the best future perspectives.
Product
The Danube Plaza is a 3*** hotel located in the center of Ruse, Bulgaria, at the main square in a vibrant area. The building, including the 134-bed hotel, a restaurant, two bars and a garden, was built in the 1960s, ever since it has undergone various renovations. However, in the last 20 years it has not been renovated. It is therefore planned to modernize and refurbish the building completely. Since the Danube Plaza is the oldest hotel in town, it is crucial to find a good mix of an image of being old-fashioned (since many locals connect the hotel to personal memories, like weddings or birthday parties) and modern (in order to attract business customers). The rooms will be provided in an excellent condition, equipped with flat screens, comfortable beds, phones, safes, soundproof windows, furniture, mini-bar, and frills like pens and writing pads. Additionally, small and large conference rooms are going to be established, so as to provide business customers with an excellent offer. Major and minor events in the restaurant complete the value proposition of the business.
Legal Structure
Today, the Danube Plaza is one company which encompasses a hotel as well as a restaurant without any clear distinctions between the two divisions. This structure is going to be abolished: the business is going to be split up in three independent legal entities in the form of private limited companies: the real estate (holding) company, the hotel operating company and the restaurant/bar operating company, the main reasons of which are risk reduction as well as accountability of costs and revenues. All three legal entities are going to be fully owned by the current owner, Plamen Mihov, who is going to be the CEO of the Real Estate Company, while the two Operating Companies are going to be managed separately. Correspondingly to this structure the business plan includes three separate business plans, which can be presented separately to potential investors.
Business Modell
Real Estate Company
The revenues of the real estate company are in general based on the rents from the operating companies, which are calculated on the basis of the buildings net asset value as well as compensations for services. The company is basically responsible for services such as accounting.
Hotel Operating Company
The hotel operating company has two major revenue flows: the relatively low room rate and higher priced fees for additional services. With active yield management room rates are adjusted to price levels of the competition or high demand seasons, for example during congresses in town. Costs include fixed costs, including rent and personnel, and variable costs, including energy, laundry and supply costs. The main customer segment is business customers, who the offer of the hotel is geared to.
Restaurant/Bar Operating Company
The restaurant offers space for around 180 seats and is a traditional restaurant on high quality standards attracting hotel guests, tourists and residents of Ruse with higher income. The bar outside is open in the warmer seasons with space for 50 seats. The chill-out bar aims to attract a younger segment, including hotel guests, tourists and residents of Ruse. Garden Eden is located in the inner courtyard. With regard to its wellness concept the target group are young, health-conscious adults. The basic revenue stream results from consumed food and drinks. In addition private and special events provide supplemental revenue. It is crucial for Danube Plaza to succeed in positioning the restaurant as a fancy place for inhabitants, in order not to assume the bad image of a hotel restaurant.
Market and Competition
The Hotel Market
A detailed analysis of the current market conditions has shown that particularly the business customers segment is interesting for Danube Plaza. While accommodation expenses have decreased in the years of 2009 and 2010, the market is about to enlarge again, as the development of 2011 as well as future predictions have shown. The main competitors in this market segment are especially high-quality hotels, which gear their offers to the needs of business customers. Of those, six could be identified as major competitors.
The Food and Beverage (F&B) Market
Ruse disposes of a vibrant nightlife which enables many restaurants and bars to survive in a competitive market. Due to a large number of arriv- ing tourists, expenses for food as well as beverage have experienced a steady rise in the last years.
Financials
In the most likely case of future developments a positive result has already been projected for the financial year 2014. The financial analysis attached encompasses an investment amounting to € 1,000,000 for the refurbishments, which are carried out by the real estate company. A scenario analysis has shown that the business is highly volatile, which entails strong opportunities and risks for the company.
Cooperation Partner
Hotel Management JSC
E hotel@danubeplaza.bg
Student Team
Pál Blaskó
Bernhard Grabner
Philipp Karbun
Laura Mazzuchelli
N.N.
Wintersemester 2011/12
Executive Summary
Great ideas are born within MSF* every day.
How can this innovative potential be managed?
MSFers from all over the world have great ideas and innovative suggestions on how to do an even better job on a daily basis. Unfortunately, most ideas never reach the implementation phase.
The overall objective of the project thus was to implement a system that helps that promising ideas and innovative suggestions arising by employees, volunteers and members of MSF (primarily those in the ield) are used to improve MSF’s solutions for both medical and non-medical problems.
Even though the idea submission process is very important, this project is not only about gathering suggestions from MSFers. It is about creating a holistic idea management system that bears innovative fruit. It has to create an innovation-friendly organizational culture, in which employees and volunteers of MSF are motivated to contribute their ideas, to select the most promising ideas, and to implement them.
Four questions emerged right from the beginning:
- How can the willingness of ield workers to submit their ideas be optimized?
- How can inner-organizational support to implement such a system be achieved?
- How can be assured that (only) promising ideas are pursued after they have been submitted?
- How can ideas travel both up and down the information channels?
Methodological approach
The project team’s approach to answering these four central questions was inspired by Chesbrough’s relexive relationship between internal and external lows affecting open innovation.
MSF research reports on innovation, a rigorous analysis of MSF’s organizational structure together with the project partner, an expert survey including 65 MSFers (conducted online due to the fact that they were scattered all over the world) allowed for an internal perspective. Additionally, the lecture of according literature (focussing on innovation management in NPOs and open innovation), other surveys with 25 external experts, 5 interviews examining the approach toward innovation in comparable NPOs, and a number of case studies exploring for-proit solutions added an external perspective.
Evaluating different scenarios
The indings from the research phase (especially owing to a surprisingly high response rate of around 45% in the expert survey) proved to be highly valuable.
First and foremost, it became clear that there are seven different choices to make:
the medium (e.g. Internet or on paper),
the arrangement of the idea submission (e.g. at random or by answering a question posed by the headquarter),
the mode of evaluation (e.g. via an expert committee or by a crowd),
the innovation culture (are there e.g. regular MSF innovation days?),
the degree of cooperation (e.g. with corporate actors or former MS Fers),
finance (can one donate an idea?)
and rights (creative commons vs. conservative terms and conditions).
The final recommendation was based on six criteria (visibility, complexity, openness, structural independence, flexibility, resistance to implementation) mainly drawn from best-practice cases and MSF’s organizational culture, which differs greatly from traditional companies. By evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of four ideal scenarios (national staff idea generator, internal idea management system, lean public submission tool, open innovation machine), the project team concluded on one possible system that combines all strengths.
It incorporates a public internet platform with two variably demanding interfaces (depending on the connection strength), the possibility to ask for ideas in certain areas, an open review process, and creative commons licences. Additionally, several recommendations concerning the creation of an innovation culture within MSF were made.
Cooperation Partner
Médicins sans Frontières
(Ärzte ohne Grenzen)
Taborstrasse 10
1020 Wien
ÖsterreichContact Person
Andreas Papp
Edith Rogenhofer, MSc
Tel.: +43 (1) 409 72 76
E-Mail: andreas.papp@vienna.msf.org
Student Team
Christof Brandtner
Matthias Gerbavsits
Katharina Schermann
Wintersemester 2012 / 2013
Executive Summary
About the Partner
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is the United Nations’ global development network which helps developing countries to attract and use aid effectively.
Project goal
The aim of the project was to help UNDP to create and introduce an in- novation toolkit which will be called UN ID Book in the following report. More specifically, the goal was targeted by giving recommendations on the toolkit content as well as on the design and on the implementation of the toolkit within the structures of UNDP.
Methodology
First of all, an analysis of the current state was conducted in order to better understand the UNDP’s organizational structure, its project guide- lines and its previously faced problems. For the purpose of the problem identification interviews with project managers in Bratislava were conducted and a cause-effect analysis was completed. The main finding of the analysis was that UNDP projects highly depend on the support of their stakeholders. For the stakeholders fast and reliable solutions are therefore necessary. Other challenges identified were the insufficient knowledge and time pressure of the project managers as well as the inefficiency of UNDP-internal processes and limitedness of financial resources.
In a next step, innovation tools which would best address those above- mentioned problems were sought. In order to find those innovation tools, which would suit best to be applied in UNDP projects, approximately 50 books and articles dealing with innovation methods were screened. In the end, 17 innovation tools were selected, including tools which can be used to identify and solve problems, to generate ideas, to share knowledge and to foster user-driven innovation.
Results
All of the selected tools have then been adjusted to the specific needs of UNDP. This means that all the tools were tailored to the challenges and limitations of UNDP. For example, lead user methods were simplified so that they could be used without investing huge amounts of time and money. The explanations of the tools were kept clear and simple while proper explications on how to apply them were still provided. For each tool the feasibility was determined on basis of 6 dimensions: the time needed, the people needed, the application frequency, the complexity of the tool, the financial resources and other resources needed. The three most important dimensions (financial resources, complexity and time) were then visualized in the form of Harvey Balls. Finally, a short summary of each tool was provided and an example for a potential application area of UNDP was given.
In a last step, recommendations on the design of the toolkit and on the implementation of the toolkit were offered. Concerning the design of the toolkit, three innovative ideas were presented and explained. The selected ideas greatly differ in their required resources and their complexity. Finally, the most effective strategies for the implementation of the toolkit were determined and recommendations on the UNDP-internal communication of the toolkit were provided.
Cooperation Partner
UNDP Bratislava Regional Centre
Grosslingova 35
811 09 Bratislava
Slovak Republic
T +421-2-59337-111
E registry.sk@undp.orgContact Person
Knowledge and Innovation
Giulio Quaggiotto
Team Leader
T +421-2-59337 276
E giulio.quaggiotto@undp.org
Student Team
Christoph Fischer
Manuel Wildtgrube
Marius Höbenstreit
Julia Ebner
![[Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/wu/_processed_/b/f/csm_104-Laptop-960_v1_8833b81630.jpg)